Infectious Waste
The correct disposal of contaminated waste is a key task in order to minimize or prevent the escape of organisms from a laboratory and thus to avoid any danger to human health and the environment.
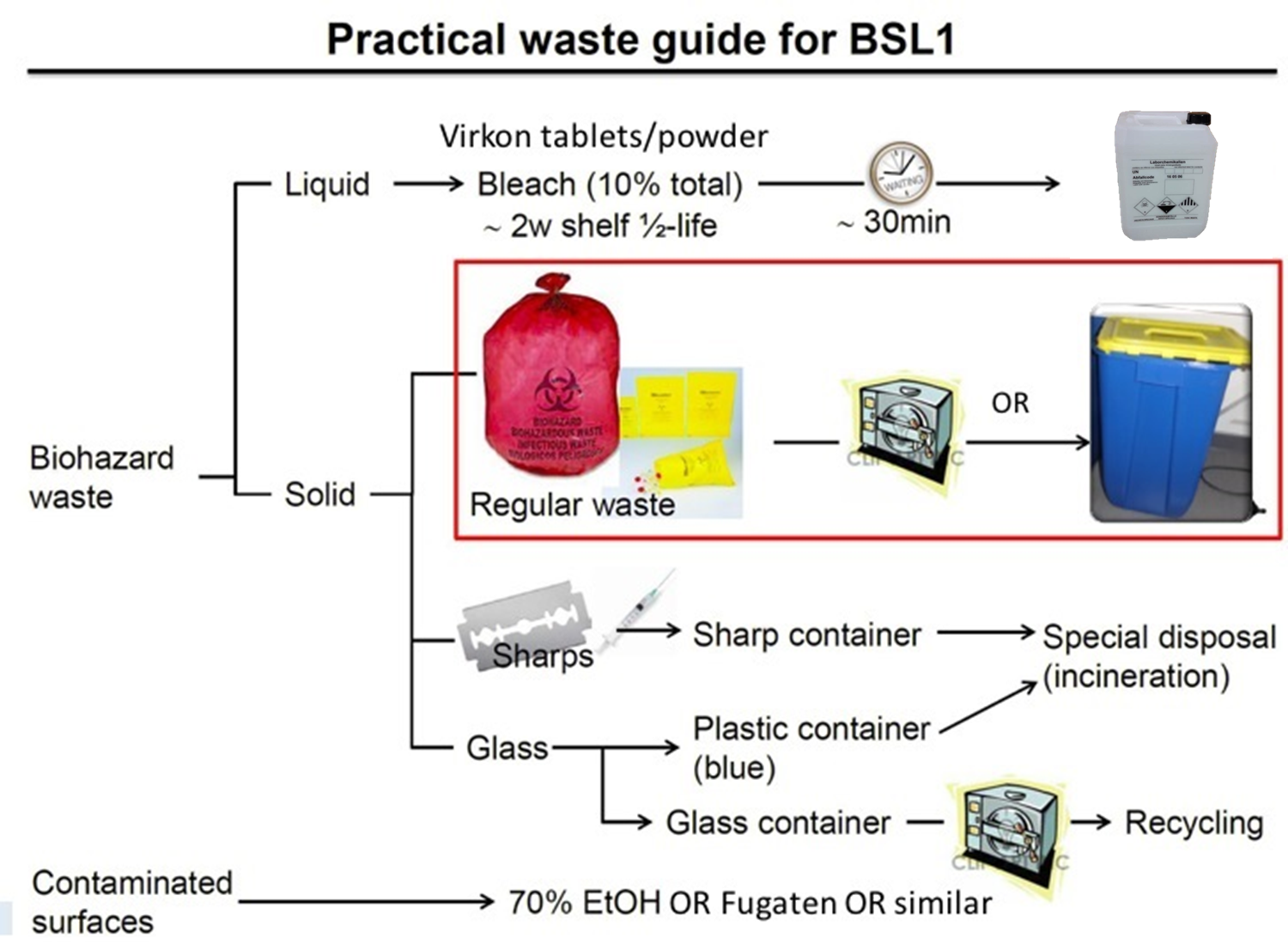
Biohazard waste: ALL materials used for cell and/or bacteria cultures (contact with cells) AND recombinant nucleic acids in all forms, natural and synthetic (e.g., DNA, RNA, shRNA, etc.) are treated as biohazard/infectious waste.
Liquid waste
Liquid biohazard waste must either be chemically inactivated or sterilized.
Chemical inactivation
Liquid biohazard waste can be inactivated e.g. with 10% bleach (final concentration) or Virkon tablets/powder according to the manufactures’ instructions.
Leaflet on chemical inactivation (AWEL, 2019) (PDF, 59KB)
Guidelines on chemical inactivation-2016 (PDF, 3.4 MB)
Products used for chemical inactivation (AWEL - 2019 (PDF, 439KB)
Attention:
Liquids containing more than 0.25% bleach are harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effect. Do not autoclave bleach.
Leaflet on water protection in laboratories (version 0.2) (PDF, 24KB)
Sterilization
Biohazard waste is sterilized by autoclaving. Only well instructed employees are allowed to operate autoclaves within the permises of the DBMR.
Solid waste
Use blue containers UN 3291 with yellow lid. They must be ordered in the central warehouse (SAP shopping cart)
Containers that are not correctly closed or dirty, are not picked up:

